Comparison and Evaluation of Methods to infer Gene Regulatory Networks from Multimodal Single-Cell Data
| Project Manager | Dr. Pau Badia i Mompel |
|---|---|
| Principal Investigator | Prof. Dr. Julio Saez Rodriguez |
| Affiliation | Heidelberg University, European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) |
| Project duration | 3/2021 - Ongoing |
| Platform used | bwForCluster Helix, SDS@hd |
| bwHPC Domain | Medical Sciences |
| DOI of Publication | https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.12.20.629764 |
| Project added | 01.04.2025 |
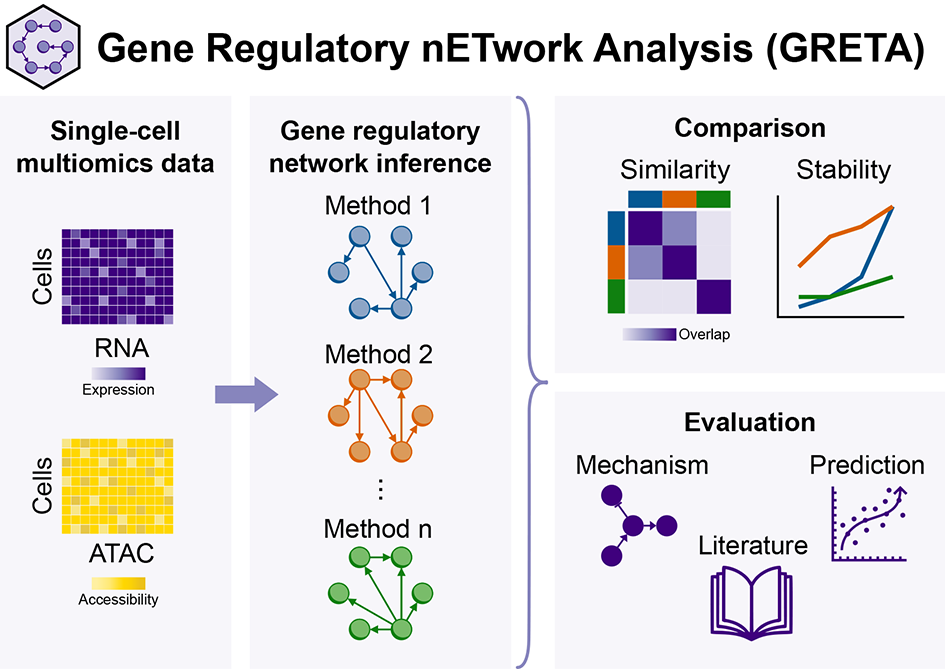
Although all cells in the human body contain the same genetic information (DNA), they look and function differently. These differences are driven by gene regulation, where some genes control others in complex networks, making some genes be expressed in some cell types but not others. We can computationally generate these networks, known as gene regulatory networks (GRNs), using new technologies that measure individual cells. While many methods exist for making GRNs, it is unclear how well they actually work. In this study, we introduce a framework to evaluate and compare these methods.
To make our results reproducible, we implemented the latest GRN inference methods in a modular pipeline using Snakemake, a workflow management tool. Our framework leverages the Helix cluster to run jobs sequentially and SDS@hd for data storage. Using cluster resources was essential for this project, as GRN analysis demands significant computational power and storage space.
With our open-source framework, GRETA, we found that while these methods can recover regulatory interactions known from past research and make predictions from observational data, they struggle to predict causal relationships after perturbations. This highlights the need for further improvements. However, our framework now serves as a solid reference for measuring progress and comparing new methods.