During proton and light ion-beam therapy, secondary neutrons are generated and can contribute to unwanted dose to the patient. With the ultimate goal of improving the outcomes of the treatments for cancer patients, this paper investigated how the irradiation room influences secondary neutron dose. For this, measurements done with active neutron detectors were compared to computational Monte Carlo simulations performed with the room geometry.
Read more
Symmetry is one of the most fundamental ideas in physics, but its role in systems far away from their balanced, equilibrium state is less understood. Our research develops a framework to identify hidden or emergent symmetries in such quantum systems. Using ultracold atom experiments and large-scale simulations, we apply this framework to explore spontaneous symmetry breaking in nonequilibrium dynamics.
Read more
The γ-tubulin ring complex (γ-TuRC) templates the de novo assembly of microtubules from α/β-tubulin subunits and thereby dictates the dynamics, number and orientation of microtubules within cells. Using cryo-electron microscopy as a key technology, we investigated how this process is regulated by γ-TuRC activation and localization factors at the structural level.
Read more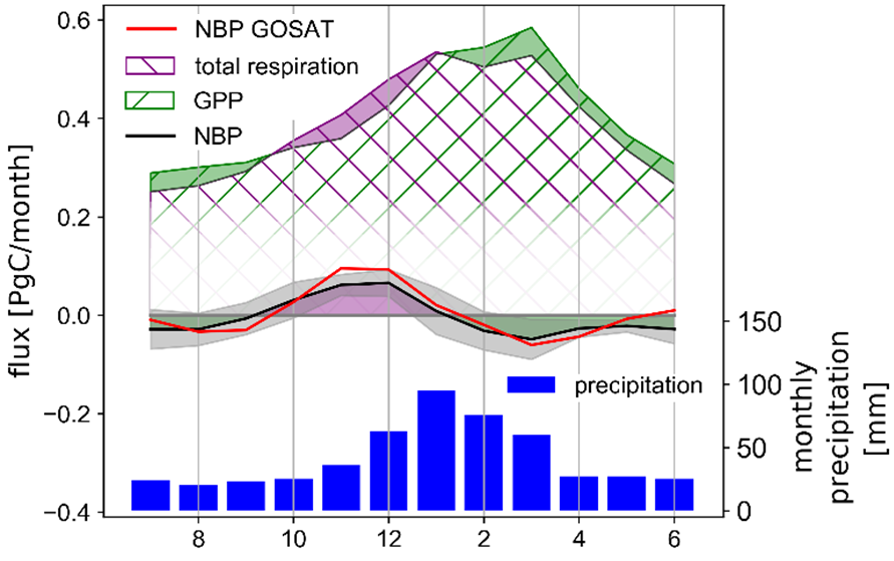
On Earth, year by year, the land biosphere takes up one third of man-made carbon dioxide emissions. Semi-arid regions control the seasonal and year-to-year variability of the biogenic uptake through their sensitivity to climate variations. Examining satellite carbon dioxide data and ecosystem models, we have discovered that microbial respiration after rewetting of dry soils drives carbon uptake variability for continental-scale regions.
Read more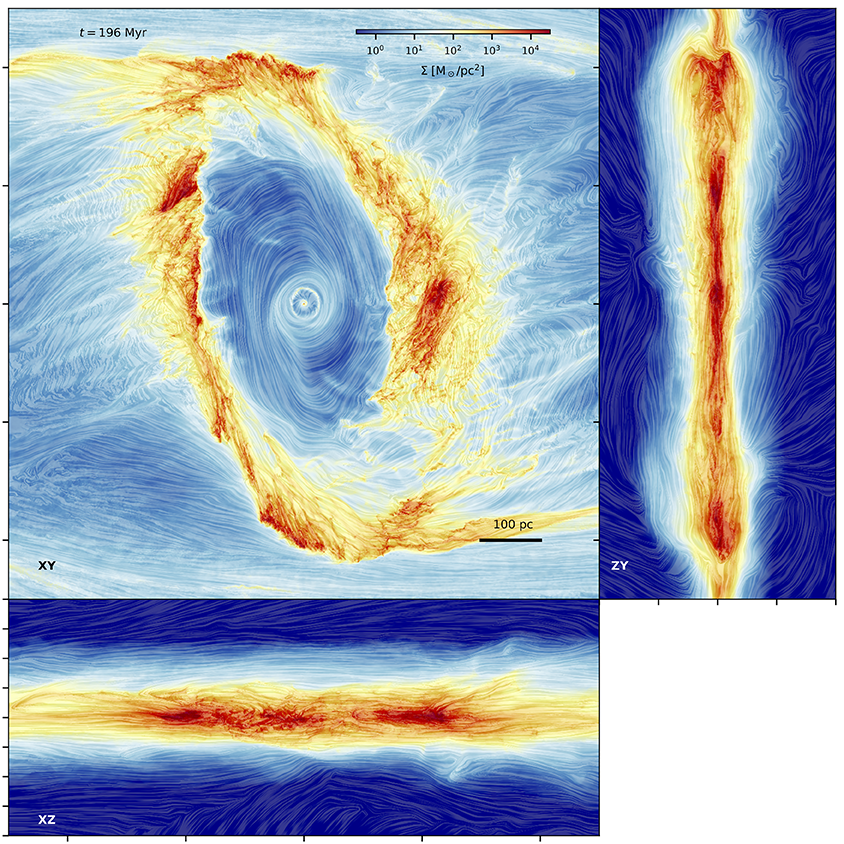
The interstellar medium in the central regions of our Milky Way is known to be strongly magnetised, but the large-scale morphology of the magnetic field and its impact on gas dynamics are not well understood. We approach this challenge by using three-dimensional multi-phase magnetohydrodynamical simulations of the gas flow in a Milky Way analogue galaxy.
Read more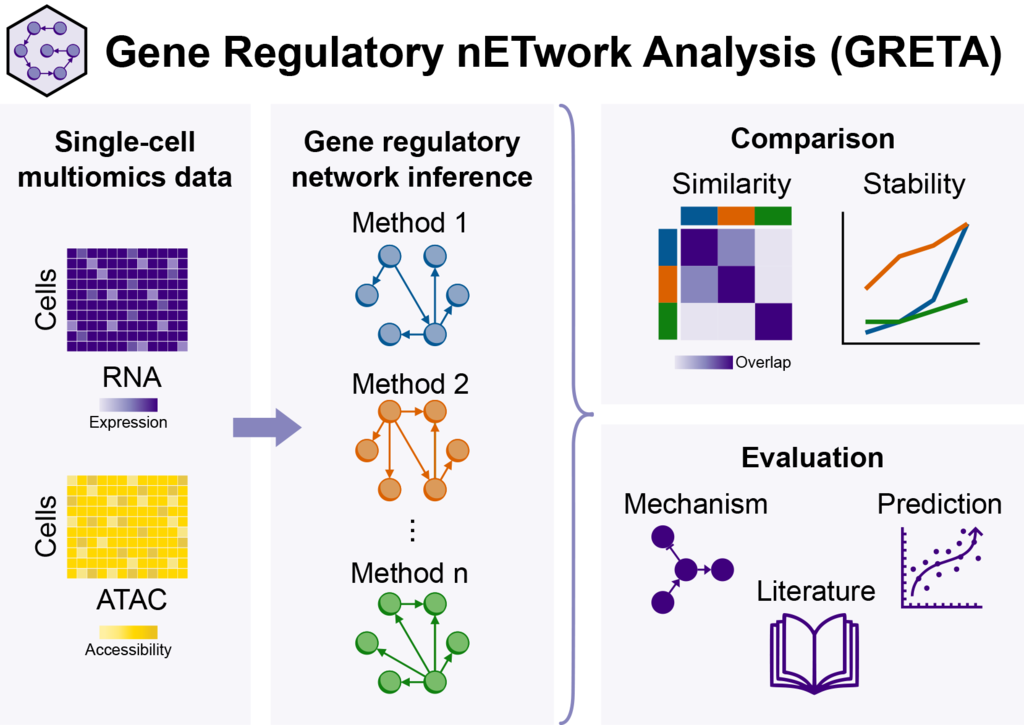
All human cells contain the same DNA, yet they look and function differently because they express different genes. This difference is driven by gene regulation, where genes interact in complex networks. Thanks to new technologies and methods, we can study these networks more closely. In this work, we introduce a framework to assess the accuracy of these methods in inferring gene regulatory networks.
Read more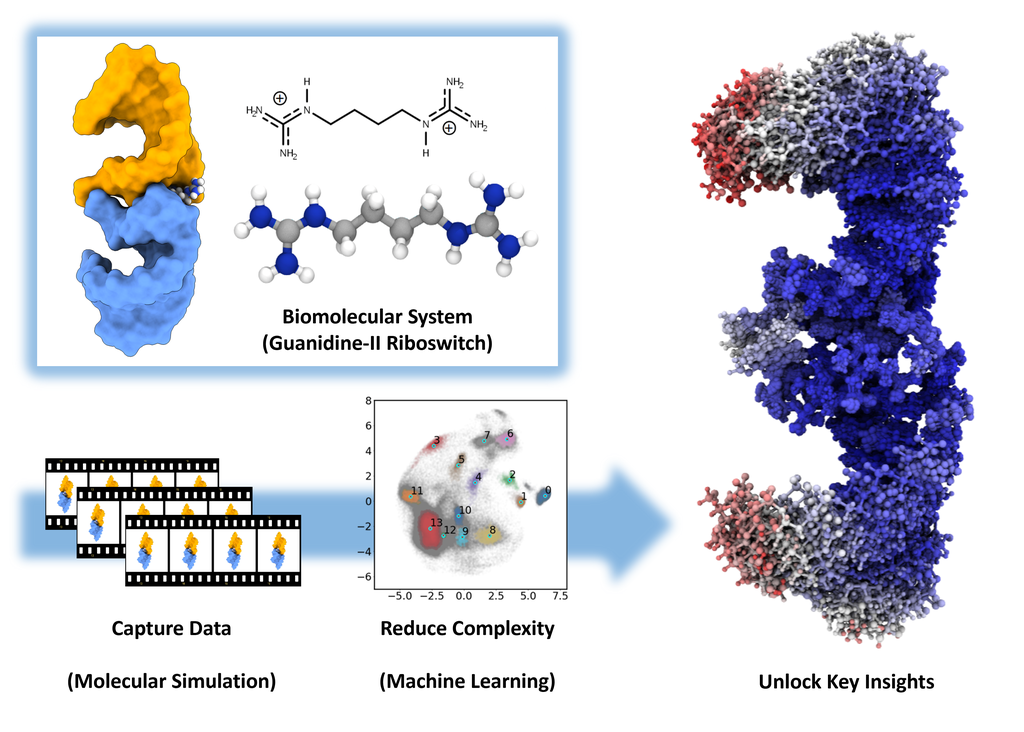
In this project, we investigated a type of RNA molecule known as riboswitches, which play an important role in controlling gene expression in bacterial cells. By using a mix of experiments, large-scale computer simulations and machine learning, we studied how the guanidine-II riboswitch changes shape when binding to specially designed molecules, offering deeper insights into how these genetic switches work.
Read more